

Australian city workers’ average commute has blown out to 66 minutes a day. How does yours compare?
The average weekly commuting time in Australia has increased considerably since 2002, and this can have negative impacts on job satisfaction and productivity, RMIT experts say.The average weekly commuting time in Australia has increased considerably since 2002. According to the latest Household, Income and Labour Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) Survey, workers averaged 3.7 hours’ commuting time per week in 2002, but this had increased to 4.5 hours by 2017.
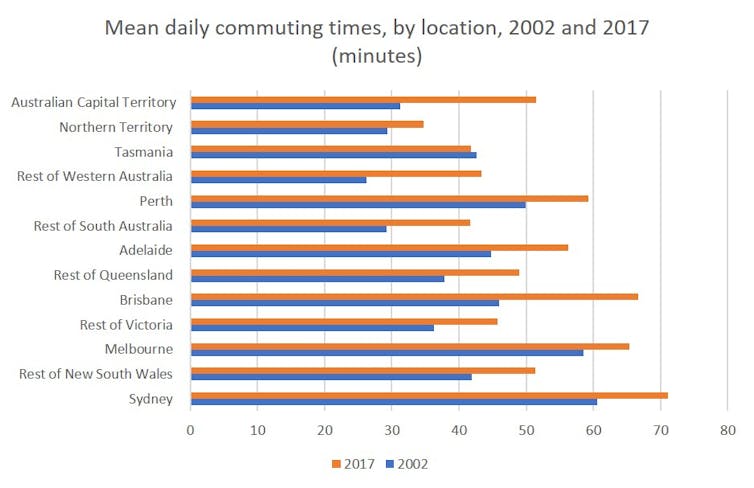
In 2017, workers in mainland state capitals (Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Adelaide, Perth) had consistently longer commute times than those living elsewhere. These city workers typically spent more than an hour travelling to and from work each day. The average was about 66 minutes. This is a 20 percent increase from the average of around 55 minutes in 2002.
As in past surveys, Sydney had the longest average daily commutes (71 minutes). In 2017, it was followed by Brisbane (67 minutes), Melbourne (65 minutes), Perth (59 minutes) and Adelaide (56 minutes). Reasons for the increasing commute time vary among different cities but may include increased road congestion, urban expansion and poor public transport services.
Average daily commuting times across Australia also increased from about 49 minutes in 2002 to almost one hour in 2017.

Workers in the Northern Territory had the shortest commutes in 2017, averaging close to 35 minutes per day.
The HILDA analysis covers all workers aged 15 years and older. This includes those with commuting times of zero (that is, who work from home).
The survey, based on interviews with about 17,000 Australians yearly, also reveals that the share of people commuting two or more hours a day is increasing, from 12 percent in 2002 to 18 percent in 2017. Men are more likely than women to be long-distance commuters. And middle-aged workers (aged 25-54) are more likely to have long commutes than younger and older workers.
Interestingly, fathers of two children had the highest likelihood (27 percent) of having long commutes, while mothers with two children were the least likely (less than 13 percent). On the one hand, households with dependent children are more likely to live in suburban locations for the larger houses, potentially increasing commuting distance for workers in these households. On the other hand, female workers’ relatively lower wage rate and more household responsibilities, such as child rearing, may restrict them to choosing jobs closer to home.
Impacts on job satisfaction
According to the HILDA Survey, long-distance commuters (two hours or more a day) are less likely than short-distance commuters (less than one hour) to be satisfied with their working hours, work-life balance and even pay. Therefore, they have lower levels of overall job satisfaction. These long-distance commuters are more likely to quit or lose their jobs within the next year.
These results from the HILDA Survey align well with the findings of our research. Our findings suggest longer commutes not only impose physical and mental strains on workers but may also affect their work participation, engagement and productivity.
Read more: Walking and cycling to work makes commuters happier and more productive
Negative impacts go beyond work
A growing number of studies have found long-duration commuting can reduce the time a person has for other activities. These other activities, such as physical exercise, time with family, social activities and so on, are important for psychological well-being.
Lengthy commuting also potentially increases exposure to nuisances and hazards such as traffic noise, crowds, congestion, pollution and uncomfortably hot or cold conditions. These can cause physical or emotional distress and have a direct influence on people’s physical and mental health.
What can policymakers do about this?
A better balance of jobs and housing within a smaller geographic area could help to shorten commuting distances and time. Planning policy such as polycentric cities – with multiple activity centres – have been proposed in Sydney and Melbourne, and could help achieve this.
Read more: How close is Sydney to the vision of creating three 30-minutes cities?
Read more: Our growing big cities need new centres of employment – here’s Melbourne’s chance
Most Australians still rely on their cars for daily commuting. Aside from long travel distance, traffic congestion is another important factor in increasing commuting times. Encouraging alternative travel modes for commuting could potentially relieve congestion.
The HILDA Survey reveals that close to 28 percent of workers live and work in the same postcode. About 55 percent of workers live within 10 kilometres of their place of work. This suggests there is huge potential to promote active travel – cycling and walking – for daily commuting trips. Only for a minority (11 percent) are the postcodes of the home and place of work 30 or more kilometres apart.
High-frequency and reliable rapid public transport networks linking major residential and employment centres could encourage more medium and long-distance commuters to use public transport for daily commuting.
Finally, emerging transport technology, such as autonomous vehicles, is also promising to curb traffic congestion and reduce the “perceived” commuting time, if these vehicles are shared rather than owned by individuals.
Companies also have a role to play in helping to reduce commuting times and their impact on workers’ well-being. Flexible working times, which allow employees to avoid peak-hour travel, and a supportive company culture for working from home can help reduce weekly commuting time. In return, companies potentially benefit from improving employee job satisfaction and retention rates.
Runing Ye, Research Fellow, Melbourne School of Design, University of Melbourne and Liang Ma, Vice-Chancellor's Postdoctoral Research Fellow, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
- Popular Articles



