 Google Maps
Google Maps
Throughout Australia, when land is rezoned from industrial to high-rise residential, a charge is levied to help fund the required infrastructure.
In NSW it is called an infrastructure contribution.
The NSW government is reviewing it in order to cut “red tape” and “fix the uncertainty”.
They are words that ought to set off alarm bells. Queensland tells us how it is likely to play out.
A decade ago Queensland developers complained that a similar system lacked transparency and was not proportional to underlying infrastructure needs. So the Queensland government fixed it by by requiring each council to publish a standard schedule of charges based on estimated infrastructure costs.
Problem solved. Right?
No, as it happens. In 2011 the Queensland Premier suddenly announced a cap on charges. Overnight the system was disbanded and replaced with a fixed charge statewide.
Developers want lower infrastructure charges
The reality was that developers didn’t just want certainty and transparency, and they weren’t particularly keen on proportionality. They wanted lower charges.
In Victoria the property lobby is arguing for lower charges directly, without going through the charade about wanting less uncertainty and red tape.
To see the value of lower charges for developers, consider that current contributions in NSW are usually in the range of A$20,000 to A$70,000 per new apartment.
Read more: Four ways we can clean up corruption in land rezoning
If a $50,000 charge was halved, for example, it would create a $2.5 million windfall for the owner of a site who developed 100 apartments. Add that up across all the sites owned by developers and it comes to billions.
Yet they are enriched by rezoning
It’s not as if developers can’t afford what’s charged. The moment their properties are rezoned they make much, much more.
Here’s an example.
A well-situated industrial site in Sydney’s inner west was bought for $8.5 million, rezoned high density residential, then sold again for $48.5 million. The 470% windfall was the result of a government decision: rezoning.
 The rezoned site of the Lewisham Estates in Sydney’s inner west. Inner West Council
The rezoned site of the Lewisham Estates in Sydney’s inner west. Inner West Council
Not only are these windfalls enormous, they can add to the cost of infrastructure.
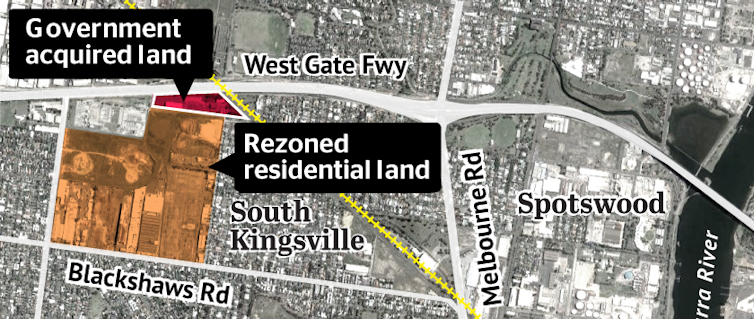
An industrial site in Altona North in Melbourne was bought by a developer for $8.7 million, rezoned for “comprehensive development” and then compulsorily acquired by the Victorian government for the West Gate Tunnel project for $22.5 million.
The Altona North rezoning added $14 million to the cost of the tunnel.
 Rezoned industrial land in Altona North. The Age
Rezoned industrial land in Altona North. The Age
Why not charge for rezoning?
The simplest way to fund council infrastructure would be to remove all fees and charges and sell the property rights granted through rezoning at market prices.
It could raise eight times what infrastructure charges do.
We know it can be done because the Australian Capital Territory has been doing it since 1971, charging 75% of the market price for new property rights granted through rezoning.
Read more: Property developers pay developer charges, that’s why they argue against them
In Sao Paulo, Brazil, the rights to develop to at higher densities have to be bought from the government at auction.
Developers won’t like it. Yet it would give them what they say they want, which is certainty. More than anyone else, they are acutely aware of what rezoning does to the value of their properties.
Cameron Murray, Research Fellow - Henry Halloran Trust, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Image: Wikipedia

