
World-first research confirms Australia’s forests became catastrophic fire risk after British invasion
Australia’s forests now carry far more flammable fuel than before British invasion, our research shows, revealing the catastrophic risk created by non-Indigenous bushfire management approaches.Australia’s forests now carry far more flammable fuel than before British invasion, our research shows, revealing the catastrophic risk created by non-Indigenous bushfire management approaches.
Contemporary approaches to forest management in Australia are based on suppression – extinguishing bushfires once they’ve started, or seeking to prevent them through hazard-reduction burning.
This differs from the approach of Indigenous Australians who’ve developed sophisticated relationships with fire over tens of thousands of years. They minimise bushfire risk through frequent low-intensity burning – in contrast to the current scenario of random, high-intensity fires.
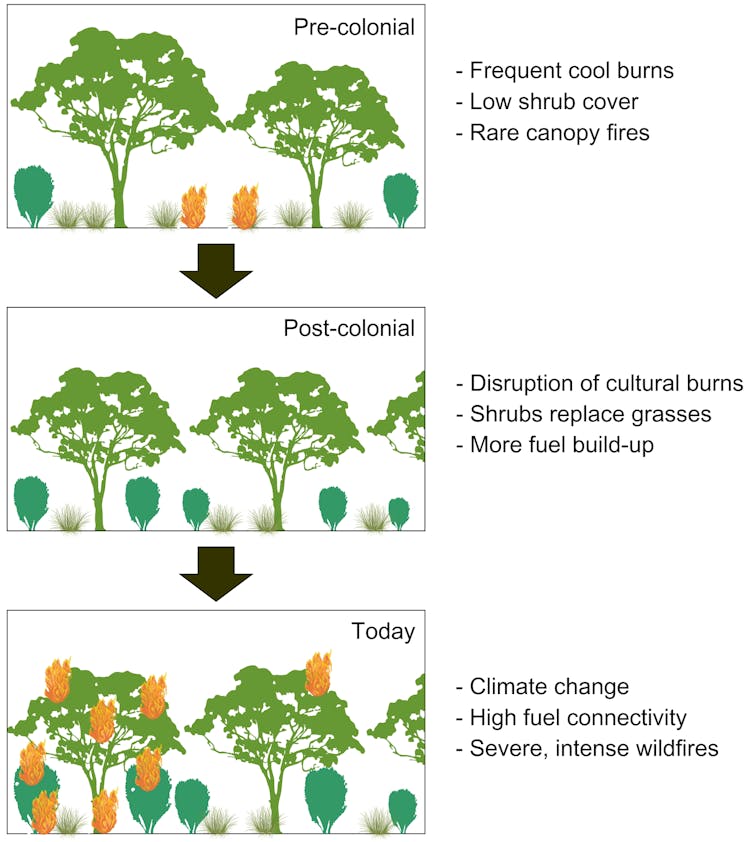
Our research, released today, provides what we believe is the first quantitative evidence that forests and woodlands across southeast Australia contained fewer shrubs and more grass before colonisation. This suggests Indigenous fire management holds the key to a safer, more sustainable future on our flammable continent.
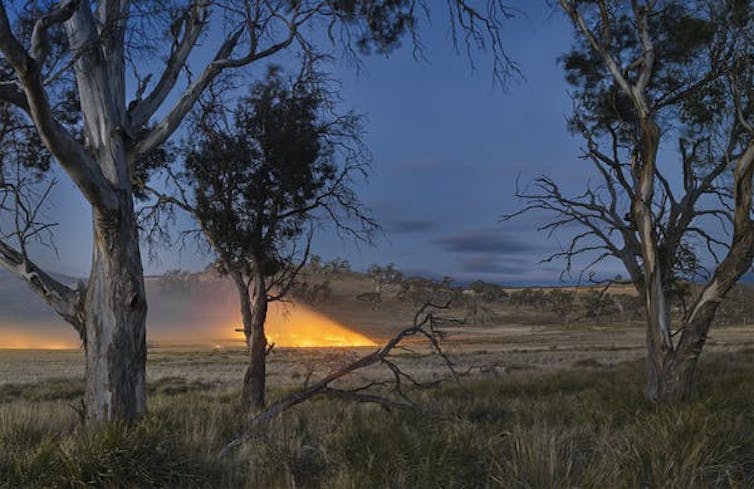

Not just a climate story
Globally, climate change is causing catastrophic fire weather more often. In Australia, long-term drought and high temperatures were blamed for the Black Summer bushfires in the summer of 2019-20. This event burned 18 million hectares, an area almost twice the size of England.
The unusually high fire extent in forests prompted several important questions. Could these massive fires be explained by climate change alone? Or was the way we manage forests also affecting fire behaviour?
Recent catastrophic fires in Australia and North America prompted renewed scrutiny of how the disruption and exclusion of First Nations’ burning practices has affected forest fuel loads.
Fuel load refers to the amount of flammable organic matter in vegetation such as leaves, twigs, branches and trunks. Large fuel loads in the shrubby layers of vegetation enable flames to more easily reach tree canopies, causing intense and dangerous “crown” fires.
Long before British invasion of southeast Australia in 1788, Indigenous people managed Australia’s flammable vegetation with “cultural burning” practices. These involved frequent, low-intensity fires which led to a fine-grained vegetation mosaic comprising grassy areas and scattered trees.
Landscapes managed in this way were less prone to destructive fires.
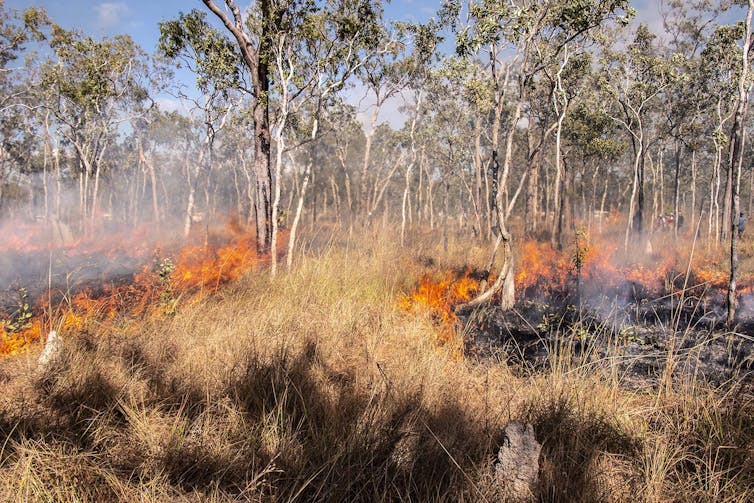

But under colonial rule, Aboriginal people were dispossessed of their lands and often prevented from carrying out many important practices.
The colonisers suppressed Indigenous cultural burning – sometimes to protect fences – causing the land to become overgrown with shrubs.
Colonial vegetation management involved clear-cutting and intense intentional burning to create land on the plains for agriculture. Forests in rugged and less desirable terrain were left unmanaged or exploited through logging.
A fire-fighting mentality came to dominate fire management in Australia, in which fires are seen as a threat to be prevented, or stopped once they start. This thinking underlies mainstream fire and land management to this day.
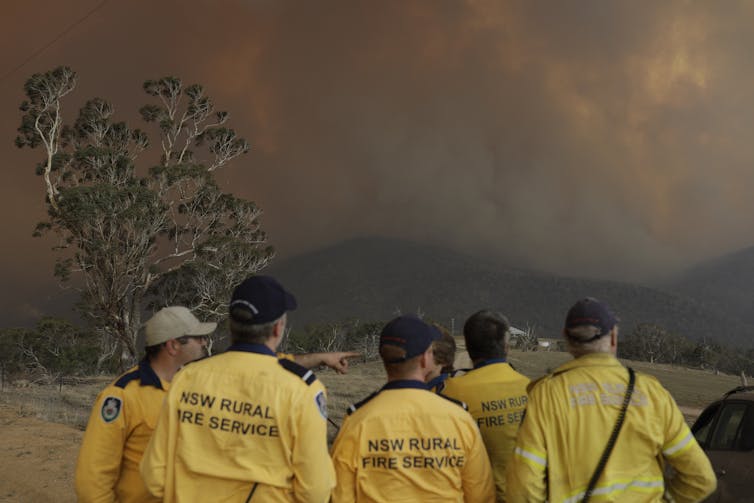

Uncovering past landscapes
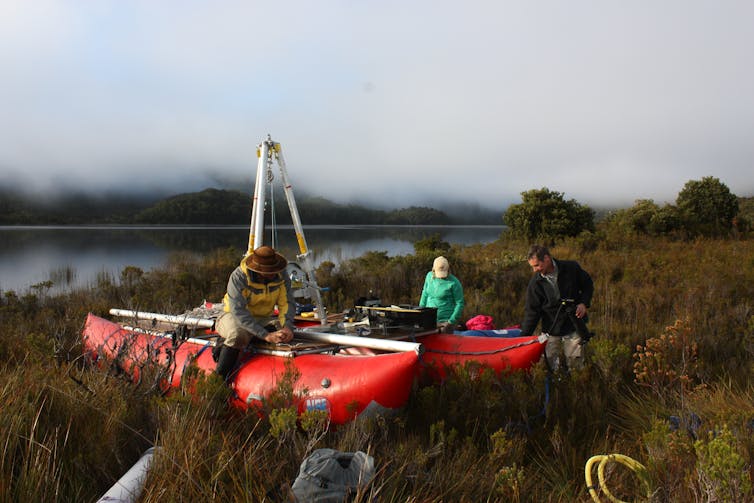
Our research set out to examine vegetation change at 52 sites across much of Australia’s southeast before and after colonisation in 1788. A large proportion of these are in forested areas of Victoria and New South Wales.
Scientists can develop a picture of past vegetation by extracting tiny fossilised grains of pollen from ancient sediment in wetlands and lake beds. Different plants produce pollen grains with different shapes, so by analysing them we can reconstruct past vegetation landscapes.
We also calibrated the amount of pollen to vegetation cover, to determine the past proportions of trees, shrubs, and grasses and herbs.
We did this using new modelling techniques that allow the conversion of pollen grain counts to plant cover across the landscape. These models have been widely applied in Europe, but our work represents a first in Australia.
We could then quantify vegetation changes before and after British invasion. We found forests in the southeast are now much denser, and more flammable, than before 1788.

We found grass and herb vegetation dominated the pre-colonial period, accounting for about half the vegetation across all sites. Trees and shrubs covered about 15% and 34% of the landscape, respectively.
After British invasion, shrubbiness in forests and woodlands in southeast Australia increased by up to 48% (with an average increase of 12%). Shrubs replaced grassy areas, while tree cover has remained stable overall.
Considering the vast area covered by our analysis, the shrub increase represents a massive accumulation of fuel loads.
More than 200 years of neglect
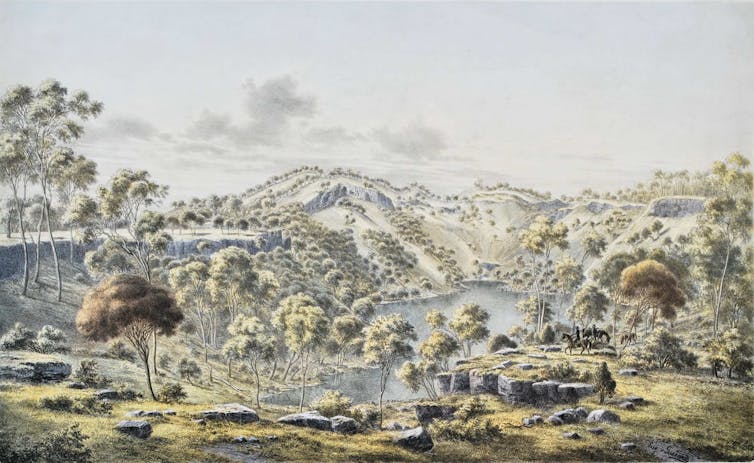
In 1770, natural history artist Sydney Parkinson described the landscape along Australia’s east coast as “free from underwood […] like a gentleman’s park”.
In 2011, historian Bill Gammage published a controversial book titled The Biggest Estate on Earth. It contained several paintings of early colonial Australia in which the landscapes resembled a savanna, with large gaps between trees and a grassy understorey.
Nowadays, many such areas are dense forest. Our research is the first region-wide analysis that gives scientific credence to these historical accounts of a landscape very different to what we see today.

The disposession of Indigenous Australians by British invaders has had a deep social and ecological impact. This includes neglect of the bush, the direct result of denying Aboriginal Australians the right to exercise their duty of care over Country, using fire.
Australia’s forests need fire, deployed by capable Indigenous hands. Without it, increased fuel loads, coupled with climate change, will create conditions for bushfires bigger and more ferocious than we’ve ever seen before.![]()
Michela Mariani, Assistant Professor in Physical Geography, University of Nottingham; Michael-Shawn Fletcher, Associate Professor in Biogeography, The University of Melbourne, and Simon Connor, Fellow in Natural History, Australian National University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
- Popular Articles



